CNC milling
Definition and explanation of CNC milling in woodworking
Milling is a shaping, machining process and, alongside turning and sanding, is one of the most common methods used to manufacture wood products. CNC milling is used to produce free forms with repeatable, computer-controlled precision. A distinction is made between 2D and 3D CNC milling.
In this article, you will learn the most important information about CNC milling. You will also read interesting facts about machinable materials and the possible applications of CNC milling in woodworking.

Table of contents
- Meaning: What is CNC milling?
- Technical basics of CNC milling in woodworking
- Variants of CNC milling in woodworking
- What materials are used for CNC wood milling?
- Fields of application for CNC wood milling machines
- Industries for CNC milling
- Which workpieces can be produced from wood with a CNC router?
- Requirements: Axes & complexity
- Advantages: Milling wood with the CNC router
- Which machines are used for CNC wood milling?
- RUWI products for woodworking
Meaning: What is CNC milling?
CNC milling means processing millable materials using a CNC machine. "CNC" stands for "Computerized Numerical Control" and means computer-aided numerical control. CNC milling is characterized by high efficiency and repeatable precision, as milling is carried out using a computer-aided control system.
Technical basics of CNC milling in woodworking
When milling in wood technology, you process edges, create contours in panels or shape any geometries from blocks of wood. A CNC router carries out these processing steps with repeat accuracy, controlled by electronics and electromechanical feeds. This saves time and manpower.
Edge processing: A wooden panel or board is guided along a fixed router head whose geometry determines the edge.
Contour milling (2D): The milling cutter plunges into a panel in a defined manner and follows a programmed contour.
Free-form milling (3D): Often carried out with a robot arm, which enables complex machining in three dimensions. The milling head sits in a spindle on the arm.
Variants of CNC milling in woodworking
Edge processing
Here you guide a board or strip past a stationary milling head. The edge shape results from the geometry of the cutter.
CNC face milling
As an alternative to dressing with planing machines, the milling cutter passes over the surface in overlapping paths. The workpiece is then turned over and milled again. This allows you to achieve a specific thickness or smooth out atypically wide parts.
Contour milling
With 2D coordinate guidance, the milling cutter plunges into the defined position and follows the desired contour. This allows external and internal contours to be milled precisely.
Free form milling
A robot arm with a milling head is often used for complex 3D designs. This process enables precise, repeatable results even with unusual free forms.
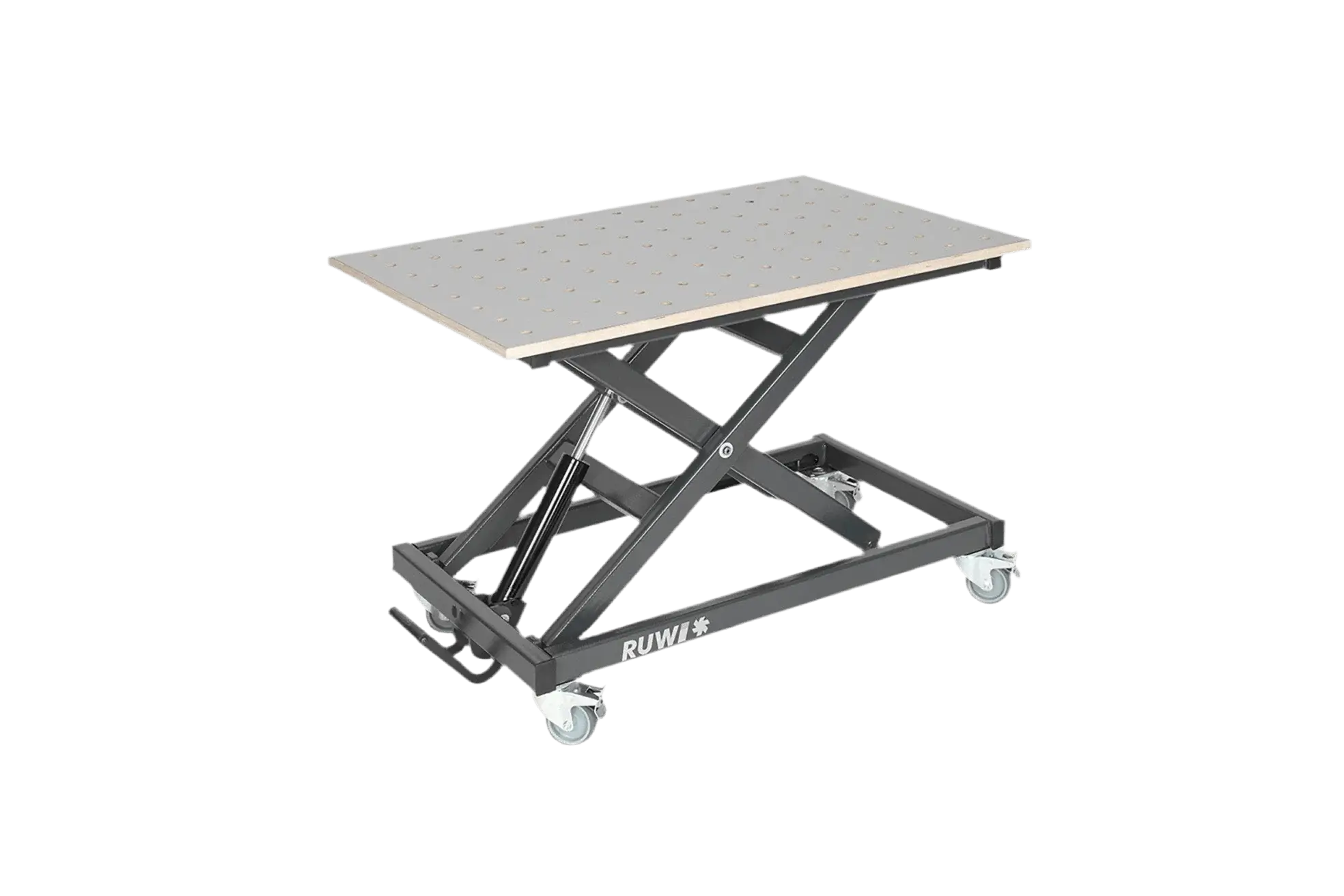
Tip: RUWI router table for CNC routing with wood
Chamfering, grooving, rounding, sanding, deburring or flush routing - a RUWI router table is a semi-stationary system that enables precise routing work on a stable work table and offers you great flexibility.
What materials are used for CNC wood milling?
Basically, you process soft, machinable materials: - Various types of wood (hardwood such as oak, beech / softwood such as pine, spruce, etc.) - Wood-based materials (MDF, chipboard, multiplex, plywood) - Plastics (e.g. CFRP, GRP), as long as there are no metallic inclusions
Metals can only be processed to a limited extent on woodworking machines, as tool and machine wear would be too high.
Fields of application for CNC wood milling machines
A CNC wood router is used to shape edges, panels or blocks. Important examples:
- Milling internal and external contours: 2D systems are inexpensive and precise.
- Nesting: All required components are machined out of a panel in a single pass.
- Drilling: Blind, slotted or through holes can be drilled automatically.
- Free-form milling: 3D machining of complex shapes, e.g. using a robot arm.

Industries for CNC milling
- Carpenter / Joiner
- Furniture, window, door and timber component manufacturers
- Caravan and motorhome conversions
- Boat building
- Model and mold making
CNC milling is universal: you only need a few manual skills, while the machine produces high-precision individual or series parts.
Which workpieces can be produced from wood with a CNC router?
This depends on whether you are processing flat or block material. You process flat material (e.g. plates) on 2D milling machines, for "voluminous" components in all spatial directions you use 3D milling machines.
- Furniture fronts and carcass parts
- 3D wooden models
- Worktops, letters, engravings
- Wooden house doors, wooden toys, cupboards
- Stair treads, windows, fences

Requirements: Axes & complexity
A 2D milling machine processes panels, but can also make deeper cuts (e.g. blind holes) to a limited extent. A 3D system with up to 5 axes masters complex components. The soft wood and the relatively large tolerances make this system technology even more flexible.
Tool changer
Automated tool change increases efficiency. The CNC control system automatically determines the replacement of milling cutters or drills. The following are common:
- Pick-up changer (few tools)
- Plate changer (medium number)
- Chain changer (large selection of tools)
Machine tables
The machine table makes a significant contribution to efficiency. Examples are
- Console tables (vacuum suction cups on movable consoles)
- Grid/matrix tables (foam rubber seal + vacuum)
- Smooth tables (for 2D and 3D, often with clamping technology)
Advantages: Milling wood with the CNC router
- Repeatable, precise and low manpower requirements
- High level of automation
- Fast processing, no loss of time
- Safety: Operator is separated from the milling cutter
Once programmed, the CNC router repeats its movements an infinite number of times. With automated loading, it runs independently in optimum operation.
Which machines are used for CNC wood milling?
- CNC machining centers
- CNC portal milling
- Single and double-column bed-type milling machines
You will also find table routers, underfloor routers or stationary routers in the woodworking sector, although these are not always CNC-controlled.
RUWI products for woodworking
RUWI offers various solutions in the field of woodworking machines. Whether you want to chamfer edges, groove, sand or flush mill - a RUWI router table is a universal addition that combines stability and flexibility.